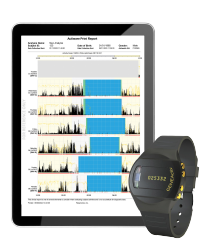
Sleep Clinical Trials Insights Unlocked with the GENEActiv
Incorporating the GENEActiv into your sleep clinical trial unlocks unparalleled depth and precision in understanding participant activity, lifestyle and sleep patterns. Unlike traditional actigraphy, the GENEActiv captures unfiltered, high-resolution raw data enabling novel digital measures that push the boundaries of insight which provide a deeper understanding of participant behaviours and treatment efficacy.
Designed for robustness, the GENEActiv ensures objective monitoring of sleep/wake behaviours and physical activity for up to two months continuously, reducing the need for frequent charging and streamlining data collection processes.
Made to rigorous medical-grade standards, the GENEActiv minimises the burden for both participants and sites. Its high-resolution tri-axial acceleration data, formatted in an open format, seamlessly integrates with any statistical software, streamlining the processing of digital measures of interest.
Validated
1500+ Publications
25+ Therapeutic Areas
200+ Clinical Trials
GENEActiv Features
Trusted by
Core Sleep Digital Measures
With the GENEActiv, you gain access to unfiltered, raw data empowering your analysis. While you can leverage this data directly, our expertise extends to processing all or part of the data for you. We specialise in developing and validating algorithms, offering tailored data processing aligned with 15 sleep digital measures to ensure relevance to your sleep clinical trial. These serve as foundational elements for potential clinical trial endpoints, significant digital health biomarkers and clinical outcome assessments.
Below is a selection of our digital sleep measures which fall in line with the core set of digital measures of sleep, as laid out by DiMe;

Total Sleep Duration
Duration of time spent sleeping in the primary sleep period.
Insufficient sleep duration is a core digital measure because it correlates with heightened all-cause mortality, obesity, cardiovascular issues, weakened immunity, and cognitive impairment. (DiMe)
Monitoring Total Sleep Duration pre-, during, and post-treatment enables researchers to gauge treatment efficacy in enhancing sleep duration and quality.
With advanced actigraphy, researchers can facilitate and monitor long-term intervention and help identify adverse effects or treatment-induced changes in sleep patterns.

Sleep onset Latency
Duration of time an individual takes to first achieve sleep after intending to sleep.
Sleep onset Latency as a core digital measure, aids in monitoring treatment effectiveness by quantifying sleep initiation, providing precise insights for researchers.
Prolonged Sleep Onset Latency disrupts sleep leading to daytime sleepiness, cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and reduced quality of life.
Monitoring Sleep onset Latency enhances research reliability, treatment efficacy assessment, and overall sleep health promotion.
Wake after Sleep onset
Total amount of time an individual spends awake after initially falling asleep and before finally waking up.
High levels of Wake After Sleep Onset (WASO) indicate fragmented sleep, leading to daytime sleepiness and diminished cognitive function. Associated with negative health outcomes like cardiovascular disease and depression, WASO serves as a crucial digital measure in clinical research.
In clinical trials, WASO offers insights into treatment efficacy by reducing sleep fragmentation. Researchers can explore WASO’s link to health outcomes including cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, mental health issues, cognitive function, and overall quality of life, paving the way for targeted interventions and improved sleep health strategies.

Number of wake events in the primary sleep period
Total number of wake events in the primary sleep period.
Frequent awakenings impair daytime functioning and well-being. Monitoring changes in awakenings pre and post-treatment aids in evaluating intervention efficacy for sleep disorders, offering valuable feedback and refining treatment strategies.
Linked to adverse health outcomes like cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment, understanding this relationship enables research to develop targeted interventions to mitigate risks.

Sleep Efficiency
Percentage of time spent sleeping when the participant intends to sleep.
Higher sleep efficiency indicates better sleep consolidation and quality, while lower efficiency suggests fragmented sleep. Disrupted sleep efficiency has been shown to correlate with adverse health outcomes like cardiovascular diseases and impaired cognition.
In clinical research, sleep efficiency quantifies sleep quality and continuity, aiding researchers in their intervention assessment.
Total napping time
Total time spent sleeping outside of the time attempting to sleep.
Prolonged daytime napping has been linked to higher risks of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, cognitive decline, and mortality.
Integrating and monitoring this digital measure into clinical research enhances the researcher’s understanding of targeted interventions.